The Special Correspondent has been over the Channel to Paris, to explore the 2013 Retromobile. As ever he finds a few gems for us to appreciate and so here we have his personal view of some cars, rare and interesting.
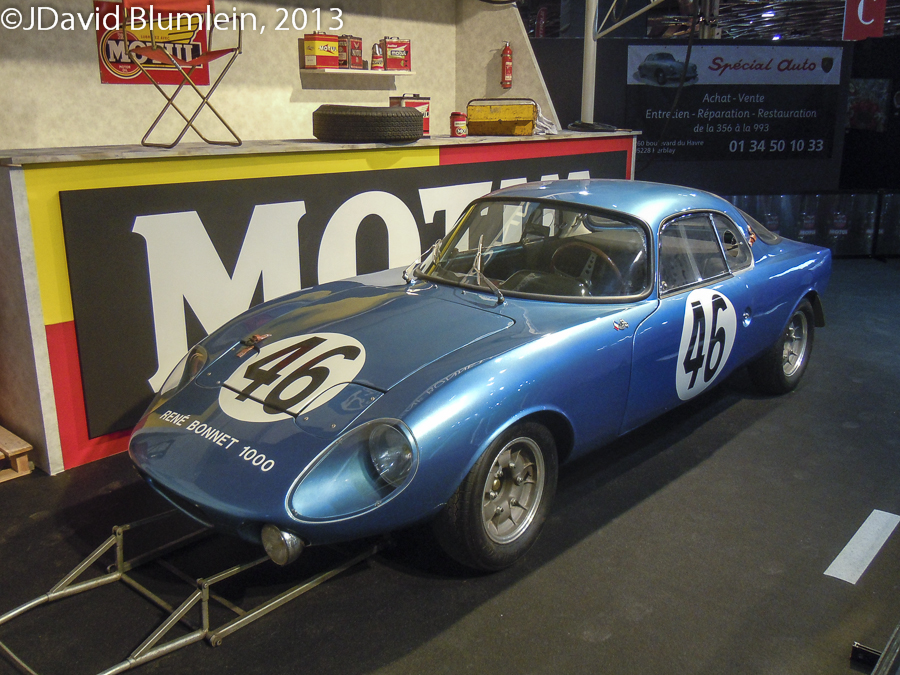
1962 René Bonnet Djet
This car represents the outcome of the break-up of the very successful DB partnership at the end of 1961 when Charles Deutsch and René Bonnet could not agree about future power-units for their cars. Deutsch went on to give the superb Panhard flat-twin its last Index of Performance win at Le Mans in 1962 with his CD Coupé while Bonnet forged an agreement with Renault.
The Djet was originally conceived to have a B.M.C. Mini engine/transmission mounted transversely amidships, a theme adopted by Chris Lawrence for his Deep Sanderson. However, the availability of the Renault engine meant the design was adapted to accommodate the French engine longitudinally, still mid-mounted.
René Bonnet number 46 finished the 1962 Le Mans race in 17th position, the first 1,000 c.c. car home, and formed the basis of a series-produced road car, the world’s first production mid-engined coupé.
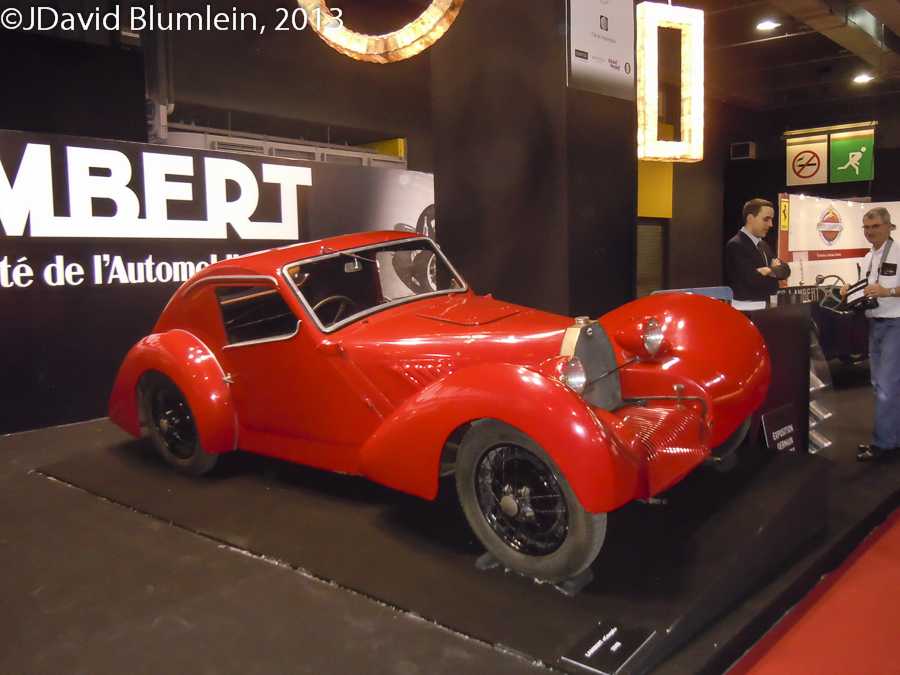
Lambert 6CV
Very few cars were made by the French engineer Germain Lambert.
Having worked for the La Buire car company in Lyon, he set up on his own in Mâcon. He moved to Reims and by 1931 had designed a chassis with front wheel drive and independent suspension by transverse leaf springs which he called “Sans Choc” because of its smooth ride. During the war he made a few electric voiturettes and then moved again to Giromagny near Belfort. Here began his most productive period. He now resorted to a more straightforward chassis with rigid axles suspended on semi-elliptic springs and presented at the 1948 Paris Salon this 1100c.c. 4-cylinder Ruby-engined 6CV Coupé. Unusually the whole front section of bonnet and wings could be raised to reveal the engine.
Lambert also made a two-seater competition model which came third in the 1100c.c. category of the 1949 Bol d’Or and second in 1951:
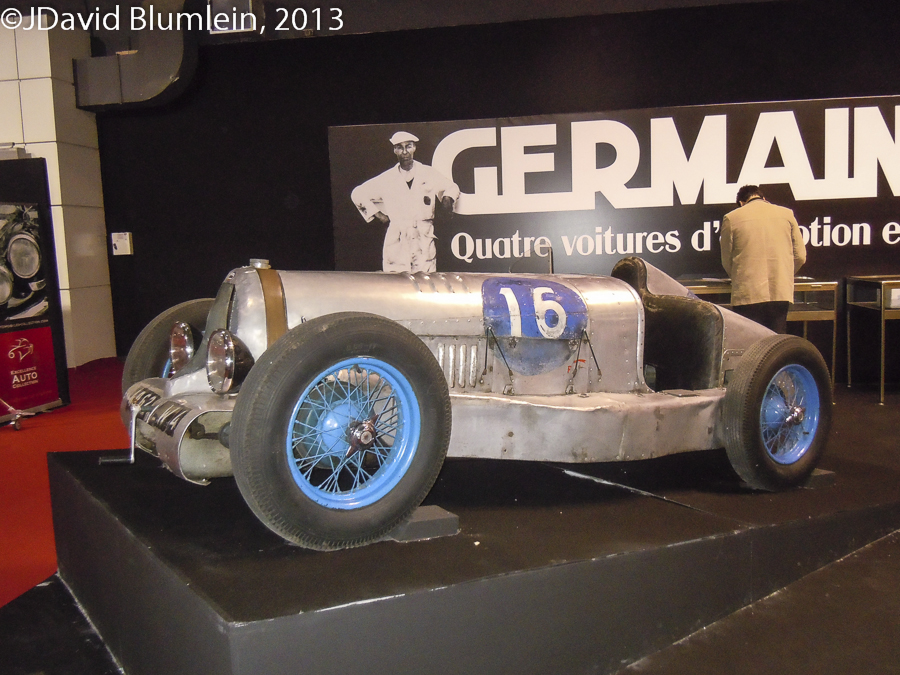

His CS Cabriolet Sport with body by Schmitt of Colmar was produced in small series and Lambert himself drove one of these to a class win in the 1953 Bol d’Or at Montlhéry.
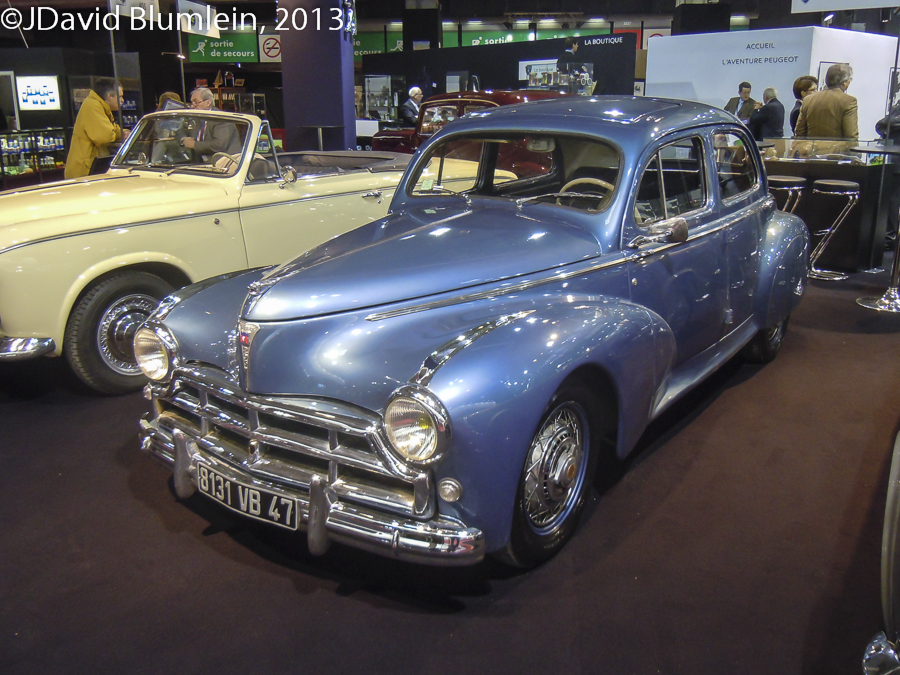
Peugeot 203 Darl’mat
Emile Darl’mat had a Peugeot agency in Paris and his firm is chiefly remembered as a low volume manufacturer of Peugeot-based sports cars in the 1930s. These cars were blessed with attractive Paulin/Pourtout bodies and in 1937 a team of three 302DS cars came 2nd, 3rd and 5th in their class at Le Mans; a year later a 402DS won the 2-litre category.
After the war Darl’mat made a streamlined 202 coupé for record breaking and then gave his attention to producing a special version of the Peugeot 203. This car had the bodywork lowered by 7cm, the engine was tuned to give 80 b.h.p. by using two carburettors and a more prominent front grille was fitted among other modifications; there was even a small dorsal fin on the boot lid. Between 1949-1950 over 120 of these were made.
It seems that Alexis Constantin used one as the basis for the supercharged 203 he ran at Le Mans in 1952.
Bugatti Type 57
The Type 57 Bugatti was presented at the 1933 Paris Salon. It was a completely new design with considerable input from Jean Bugatti and was aimed at the more luxurious Delahaye/Delage market.
Gaston Descollas, the Bugatti agent in Marseille, planned a competition programme for this car, chassis 57.300, and had the Torpedo body without hood designed and made by Dubos in Marseille.
He won the important Paris-Nice Rally and went on to win his class in that year’s French Alpine Rally. In 1936 the car received a new body, a Coach Ventoux made at Gangloff’s
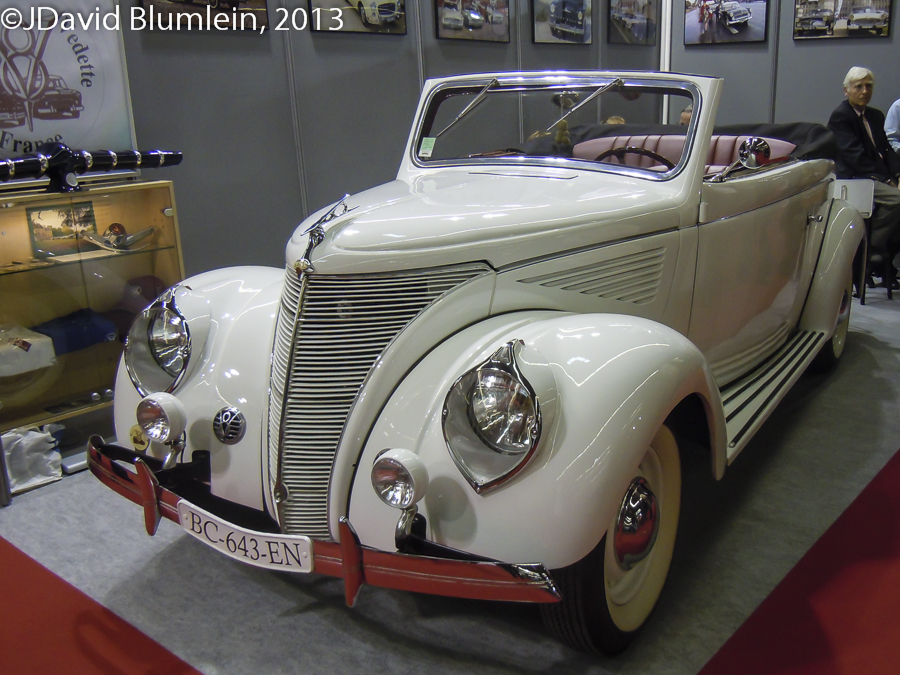
1936 Matford 3.6 V8
Mathis + Ford = Matford
Emile Mathis had been involved in the motor trade in Strasbourg since the start of the 20th century, selling a wide variety of cars to some of which he would liberally attach the Mathis name! After the Great War he became a leading maker of popular cars, producing for example over 20,000 Mathis cars by 1927, making him France’s fourth manufacturer after Citroën, Renault and Peugeot. However, despite advanced mechanical features such as hydraulic brakes in 1931, synchromesh in 1932 and independent front suspension in 1933, Mathis sales gradually declined.
Ford now came on the scene because their V8 imported from America incurred heavy import duties and in October 1934 a new company, SA Franςaise Matford, was formed whereby Ford and Mathis cars would be made side by side. But with Ford holding 60 per cent of the shares, the Mathis cars were soon squeezed out and by 1936 the Strasbourg factory was making only the French Fords, the Matfords.
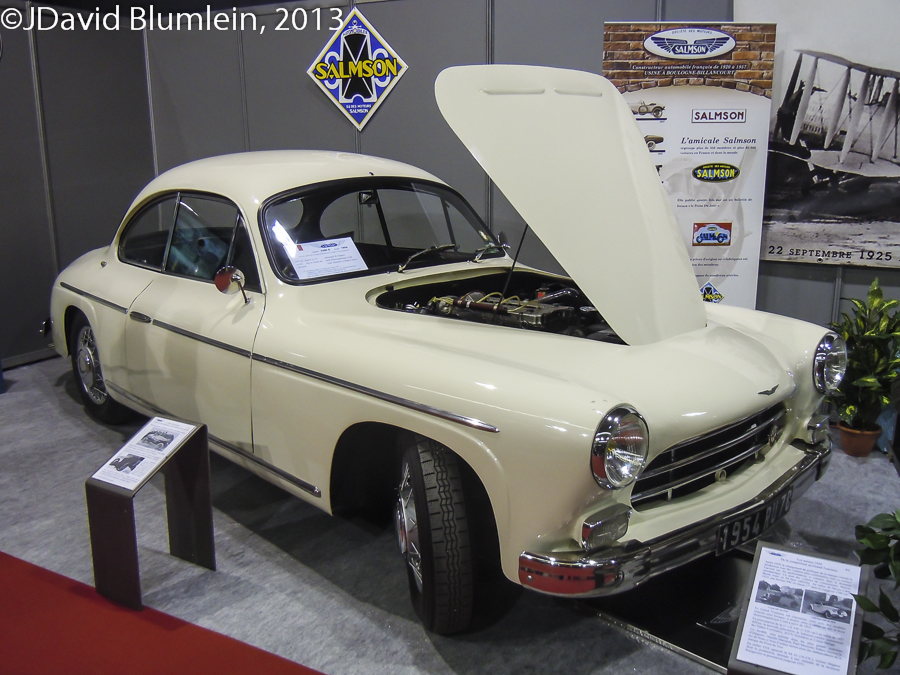
Salmson 2300 Coupé
Salmson were making aero engines at Billancourt in 1912 and produced many during the Great War after which the demand dropped. Therefore the company diversified into making cars and at first they produced the British G.N. cyclecar under licence, even supplying some to the Police Force! However, they soon developed their own sporting 1100c.c. car with engines designed by Emile Petit who also came up with an excellent 4-cylinder twin-cam unit. These cars went on to score numerous successes in competitions and two of them almost won the Le Mans race outright in 1927 when the surviving 3-litre Bentley, badly crippled by the White House crash, only just managed to stay ahead of the little Salmsons.
The 2300 Coupé, introduced at the 1953 Paris Salon, represents the final fling for the famous marque. Still with a 4-cylinder twin-cam engine and with the torsion bar independent front suspension first seen on the S4E in 1937, the 2300 performed well in rallies, achieving some fifty-five victories/class wins in both international and national events. Luck deserted them, however, at Le Mans when privately- entered cars both retired, a spyder-bodied version by Motto in 1955 and a special lightweight coach, also by Motto, in 1956.
Alas, the last 2300 came off the line in February 1957 and Salmson
cars were no more.
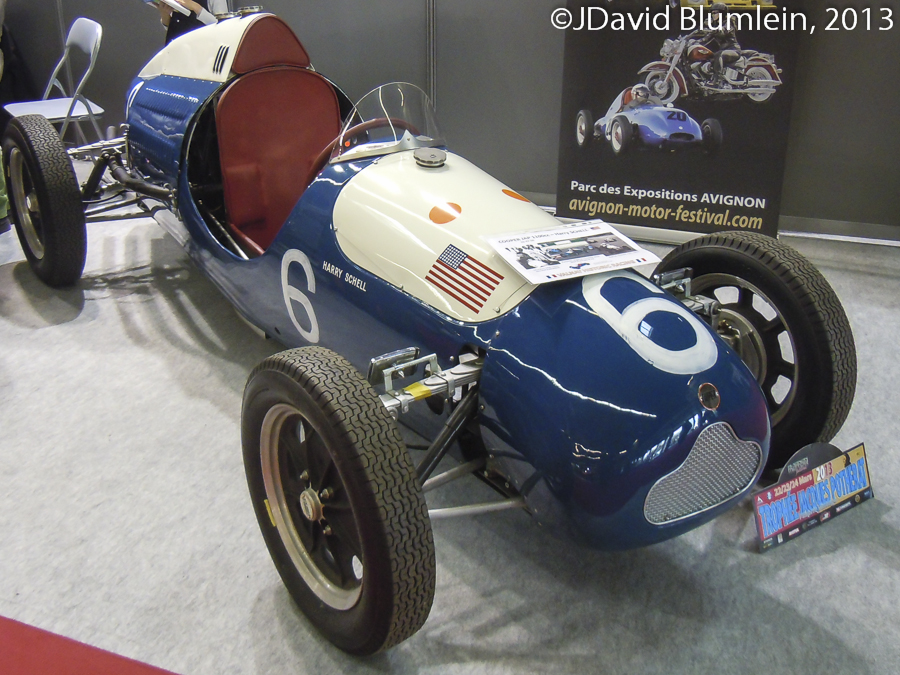
Cooper 500 Formula Three Racing Car
A hint of what was to come! When the Franco-American driver Harry Schell drove a little Cooper 500 like this but with an 1100c.c. J.A.P. twin in the 1950 Monaco Grand Prix he was making history in two respects.
First, he was giving the Cooper company its Grand Prix and World Championship début and, secondly and more significantly, he was driving the first mid-engined car to run in the World Championship. Cooper themselves were slow to develop this theme in their bigger cars (the concept wasn’t new of course – think of, for example, the 1923 Benz and the Auto Unions) and it was only with the advent of the “Bobtail” sports car in 1955 that the true benefits were realised with the advantages of modern chassis and suspension designs. When Cooper went on to dominate the Championship in 1959/60 with their mid-engined cars, everyone else naturally copied them. In the meantime Cooper had already won the Monaco GP in 1958, thanks to Maurice Trintignant’s efforts in Rob Walker’s T45.
Alas, we shall never know how well Schell’s nimble little machine coped with the big 4.5-litre and 1.5-litre supercharged cars around the twisty circuit because he was involved in the multiple shunt at the Tabac Corner on the first lap – it seems that a wave had splashed over the harbour wall very inconveniently!
TAILPIECE
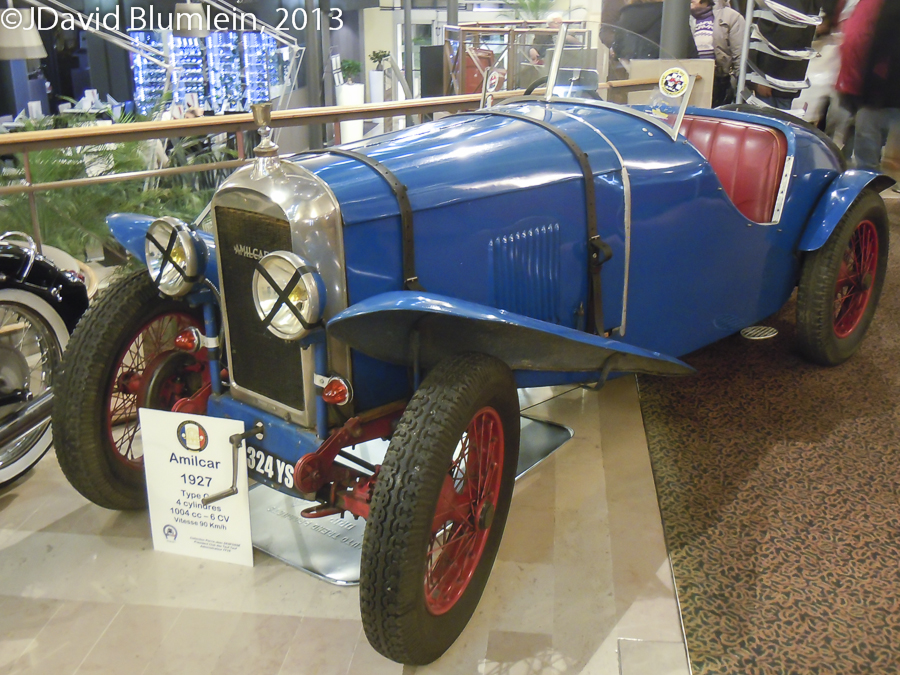

Residents of the Mercure-Porte de Versailles Expo hotel adjoining the exhibition site were greeted with this delightful little Amilcar sports car in the foyer. Last year it was a Le Zèbre – a charming gesture!
David Blumlein, February 2013